
Old Wiring Colours – Your Ultimate Guide To UK Wiring Standards
- 17 December 2023
- ,
- , Wiring
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on old wiring colours, a crucial aspect of electrical safety and knowledge for homeowners, electricians, and DIY enthusiasts in the UK. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of wiring colours used in the United Kingdom, tracing their evolution from past standards to the present day.
Whether you’re dealing with vintage wiring in an old building or ensuring compliance in a modern installation, this guide will provide you with the essential knowledge to identify, understand, and work with UK wiring colours confidently.
In the world of electrical installations, wiring colours are not just a matter of convention; they are a critical component of safety. They help in identifying the function of each wire in an electrical circuit, reducing the risk of accidents and errors during installation, maintenance, or troubleshooting. With changes in regulations and standards over the years, it has become increasingly important for anyone working with electrical systems to be well-versed in both the old and new wiring colour schemes.
As we delve into the historical overview, comparisons, technical details, and global perspectives on wiring colours, this guide will serve as your go-to resource for all things related to UK wiring standards. So, let’s embark on this journey of understanding and mastering the old wiring colours of the UK.
Key Takeaways On Electrical Wiring Colours
- Evolution of Wiring Colours: The transition from old UK wire colours to new ones aligns with European standards, enhancing safety and consistency in electrical systems.
Importance of Compliance: Adhering to current wiring regulations, such as the British Standard BS 7671, is essential for safe and efficient electrical installations.
Practical Knowledge: Understanding how to identify and work with different wiring systems is crucial, whether dealing with old wiring in renovations or new installations.
Global Standards: Recognising the variations in wiring colours across different countries is important for professionals working internationally or with imported electrical equipment.
Historical Overview of Wiring Colours in the UK
Tracing the Evolution: From Old UK Wire Colours to Modern Standards
The journey of electrical wiring colours in the UK is a tale of evolving safety standards and technological advancements. Understanding this history is not just about getting acquainted with the colour codes; it’s about appreciating the progression of electrical safety and the wiring systems that power our lives.
Pre 1977 Wiring System
In the era before 1977, the UK wiring colours followed a markedly different scheme from what most are familiar with today. The old wiring system primarily used red for live wires, black for neutral wires, and green for earth wires. This colour coding was a standard across many European countries, ensuring a constant supply of electricity in a safe and identifiable manner. However, as electrical installations became more complex, the need for a new wiring colour standard became evident.
Pre 2004 Wiring System
Moving forward to the pre-2004 era, the UK adhered to these traditional colour codes. Yet, with the integration of the UK into the European market and the introduction of the European Standard (EN), a shift in electrical wire colours was initiated to harmonize the UK’s wiring system with other European countries. This transition marked a significant shift in the UK’s approach to electrical installations, paving the way for the new UK wiring colours.
The Transition to the Current System
The current wiring colours in the UK, which were fully adopted post-2004, align with the European cable colours. The live wire colour changed from red to brown, the neutral wire from black to blue, and the earth wire retained its green and yellow colour. This transition was more than a mere change of colours; it represented an alignment with international electrotechnical commission standards, enhancing safety and consistency in electrical wiring across the UK and other European countries.
This historical overview sets the stage for a deeper understanding of why the old wiring colours in the UK were replaced with the new wiring system. As we explore further, the significance of these changes in terms of safety, compliance, and international standardisation becomes increasingly clear.
Understanding the Basics of Wiring Colours
Decoding the Essentials of UK Wiring Colours
Grasping the fundamentals of wiring colours is crucial for anyone engaged in electrical work, be it a professional electrician or a DIY enthusiast. In this section, we’ll explore the basic wiring colours used in the UK, both old and new, and understand their significance in electrical installations.
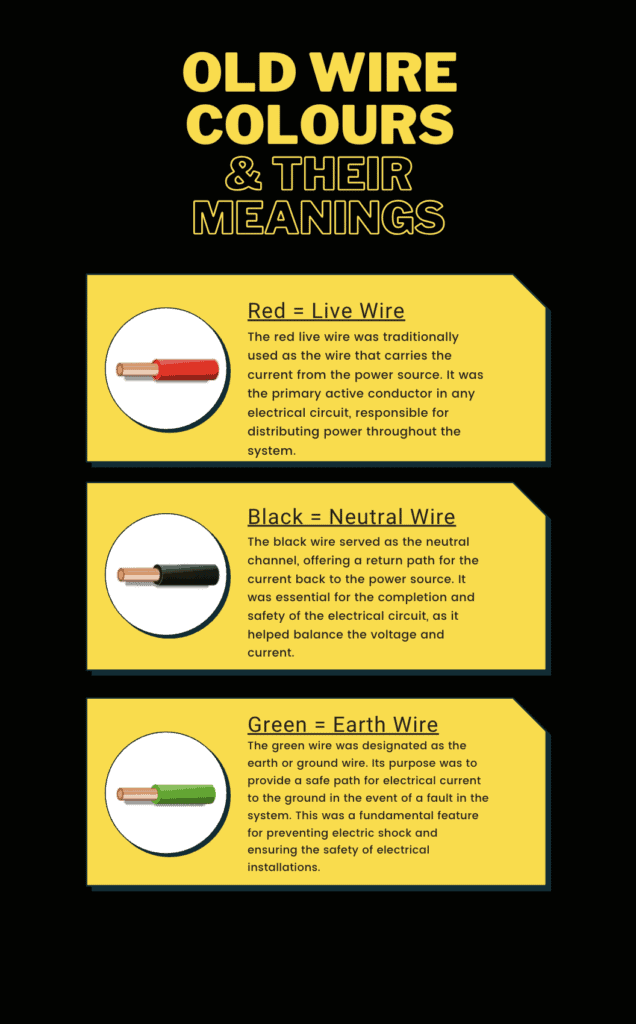
The Old and New UK Wiring Colours
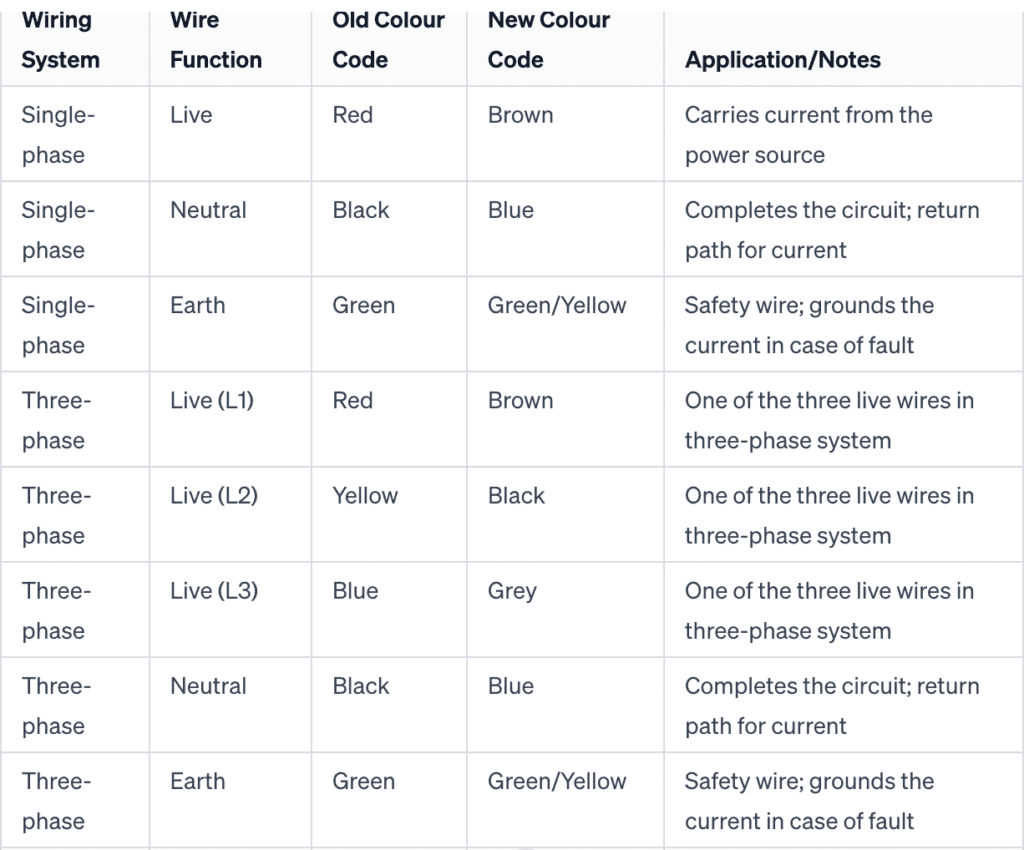
The transformation in UK wire colours is not just a matter of historical interest but a vital knowledge area for safety in electrical systems. Old wiring colours, prevalent before the change in 2004, featured a red live wire, a black neutral wire, and a green earth wire. In contrast, the new UK wiring colours adopt a brown wire for live, a blue neutral wire, and a green and yellow striped wire for earth. This shift towards new wiring colours aligns the UK with European cable colours, facilitating consistency and safety in electrical systems.
Single and Three Phase Wiring
Understanding the difference between single-phase and three-phase wiring is essential in the context of wiring colours. In single-phase wiring, commonly used in residential properties, you typically encounter the standard live (brown), neutral (blue), and earth (green and yellow) wires. In contrast, three-phase wiring, often used in commercial or industrial settings, includes additional colours like black and grey for the additional live wires, maintaining the standard blue neutral and green-yellow earth cables. These wiring systems, with their distinct colour codes, are critical for managing the higher voltage and power requirements in different settings.

Basic Wire Colours and Their Meanings
Brown = Live Wire: The brown live wire, previously red, is the wire that carries the current from the power source. It’s essential in any circuit and is a key component in safely distributing electrical power.
Blue = Neutral Wire: The blue wire acts as the neutral channel, providing a return path for the current back to the power source. Previously black, this wire is crucial for completing the electrical circuit.
Green and Yellow = Earth Wire: The earth wire, retaining its green and yellow colouring, is a safety essential. It provides a path for electrical current to ground in case of a fault, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock.
This section provides a foundational understanding of the colour codes and their roles in the UK’s electrical wiring system. Knowledge of these basics is not just a technical necessity but a cornerstone of electrical safety.
Comparison Between Old and New Wiring Colours
Understanding the Shift: Why and How UK Wiring Colours Changed
The transition from old wiring colours to new ones in the UK wasn’t merely a cosmetic update; it was a critical move towards greater safety and standardisation in electrical wiring. This section delves into the differences between the old and new wiring systems and explores the reasons behind this significant change.
Old vs New Wiring Colours
The old UK wire colours featured a red live wire, a black neutral wire, and a green earth wire. In contrast, the new wiring system, aligned with European standards, uses a brown wire for live, a blue wire for neutral, and maintains the green and yellow striped wire for earth. This change might seem subtle, but it has profound implications for the safety and clarity of electrical installations.
Why the Change in Wiring Colours?
The primary driver behind the change in wiring colours was the need for harmonisation with European standards. As the UK integrated more closely with other European countries, aligning electrical systems became essential for safety and consistency. This alignment ensures that electricians and technicians from different countries can work on systems with a familiar and standardised set of colour codes, reducing confusion and the risk of errors.
Another critical reason for the change was to enhance safety. The new colour scheme, especially the distinction between the live and neutral wires, is aimed at reducing the risk of electric shock and electrical fires. The clear differentiation helps in identifying wires correctly during installation, maintenance, and repair work, thereby minimising potential hazards.
How to Spot Old Wiring
Identifying old wiring in a building is crucial, especially in older properties or during renovation projects. Old wiring colours can indicate an outdated electrical system that may not meet current safety standards. Look for the characteristic red live wires and black neutral wires, which are telltale signs of an older wiring system. Additionally, the presence of green earth wires, as opposed to the modern green and yellow striped wires, can also indicate an older electrical installation.
Understanding these differences is vital for anyone dealing with electrical systems, whether updating an old installation or ensuring compliance in a new one. It’s also a reminder of the importance of consulting a professional electrician, especially when dealing with older wiring systems that may require upgrading to meet current wiring regulations and safety standards.
Exploring the Varieties of Electrical Cables and Their Uses
In the realm of electrical wiring, the type of cable used is as important as the colour coding. Different types of cables are designed for various applications, each with its unique set of characteristics. This section will explore the different types of wires and cables used in UK electrical installations, along with their specific colour codes.
Different Types of Wire and Cable
2-Core Wire: Commonly used for simple electrical circuits, the 2-core wire typically consists of a live and a neutral wire, often used in lighting circuits.
2-Core and Earth or 3-Core Wire: This type of cable adds an earth wire to the 2-core configuration, essential for safety in most electrical installations.
3-Core and Earth or 4-Core Wire: Used in more complex installations, this cable includes additional live wires (in different colours like black or grey) to handle more complex circuits or three-phase power.
4-Core and Earth or 5-Core Wire: Typically used in industrial or commercial settings, these cables are designed for high-demand electrical systems and often include three-phase wiring.
Specialised Cables
Tough Rubber Sheathed Cables: Known for their durability, these cables are designed to withstand harsh conditions and are often used in external or industrial environments.
Lead Sheathed Cables: Offering additional protection against moisture and physical damage, lead-sheathed cables are often found in older buildings.
PVC-insulated Sheathing: PVC cables are common in modern installations, known for their flexibility and resistance to a variety of environmental factors.
3-Phase Wiring: Understanding the Basics
Three-phase wiring is a type of power distribution that uses three alternating currents, each phase offset by one-third of a cycle. This system, common in commercial and industrial settings, efficiently handles higher loads. The wiring colours for three-phase systems include the standard brown (live), blue (neutral), and green-yellow (earth), with additional live wires typically coloured black and grey. Understanding these colour codes is crucial for anyone working on or designing three-phase electrical systems.
This section provides an overview of the various types of electrical cables and their applications in the UK wiring system. Each cable type, with its specific set of wire colours, plays a distinct role in the safe and efficient distribution of electrical power.
Safety and Compliance in Electrical Wiring
Prioritising Safety Standards and Regulations in Electrical Installations
Ensuring safety and adhering to regulations are paramount in any electrical installation. This section highlights the importance of updated wiring and the regulatory framework governing electrical installations in the UK.
The Importance of Up-to-Date Wiring
Outdated or old wiring not only poses a risk of electric shock and fire but also may not comply with current electrical regulations. It’s essential to regularly assess the condition of electrical installations, especially in older properties. Upgrading to new wiring colours and systems isn’t just about compliance; it’s a crucial step towards ensuring the safety of inhabitants and the functionality of electrical systems. Regular checks by a professional electrician can identify issues like bare conductors, old wires, or outdated fuse boards that require attention.
Does Old Wiring Need to Be Replaced?
While old wiring colours themselves aren’t inherently dangerous, they often indicate an older electrical system that might not meet modern safety standards. The decision to replace old wiring should be based on its condition, capacity to handle current electrical demands, and compliance with wiring regulations. In many cases, updating to new UK wiring colours and systems enhances safety and efficiency.
Rules and Regulations for Electrical Work in the UK
The UK follows stringent wiring regulations outlined in the British Standard BS 7671. These regulations cover everything from the correct use of wiring colours to the installation of circuit breakers and consumer units. They ensure that electrical installations are safe, efficient, and capable of handling the demands of modern electrical appliances. Compliance with these standards is not just a legal requirement but a responsibility to maintain the safety and integrity of electrical systems.
Understanding the significance of safety and compliance in electrical wiring is crucial. It involves more than just knowing the wiring colours; it’s about ensuring that every aspect of an electrical installation meets the highest safety standards.
Practical Guide for Handling Wiring
Effective Strategies for Managing Old and New Wiring Systems
Handling electrical wiring, whether in a new installation or when dealing with existing systems, requires knowledge, caution, and adherence to safety standards. This section provides practical advice for identifying, managing, and upgrading wiring systems in the UK.
How to Identify and Handle Old Wiring
Identifying old wiring is crucial, especially in older buildings or during renovations. Look for the old wiring colours: red for live wires, black for neutral wires, and plain green for earth wires. If these colours are present, it’s likely the wiring system predates the 2004 regulations. Handling old wiring should be done with care. Always turn off the power at the main switch and, if in doubt, consult a professional electrician. Old wiring might not just be about colour changes; it could involve outdated materials like cloth-insulated or lead-sheathed cables, which require special handling.
Adding New Colour Wires to Existing Circuits With Old Colour Wires
Integrating new wiring colours into existing circuits with old colour wires can be challenging. It’s essential to clearly label all wires at both ends of the circuit to avoid confusion. Using a cable with the new colour codes (brown, blue, and green-yellow) alongside old cables requires careful identification and documentation to ensure future safety and maintenance ease. Again, consulting with a professional electrician is advised to ensure compliance with current wiring regulations.
Safety Precautions When Dealing with Wiring
Safety is paramount when working with electrical installations. Always ensure the power is off before starting any work, and use a voltage tester to confirm the wires are not live. Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves and eye protection, and avoid working alone. Be mindful of the risks, such as electric shock or creating a fire hazard, and always prioritise safety over convenience.
This practical guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to safely and effectively manage wiring systems in the UK, whether you’re dealing with old or new wiring colours. Understanding these practical aspects ensures not only compliance with regulations but also the safety of those who use and interact with these electrical systems.
Global Perspective on Wiring Colours
Comparing UK Wiring Standards with International Practices
Electrical wiring colours are not uniform worldwide; they vary depending on regional standards and practices. This section offers a glimpse into how UK wiring standards compare with those in other countries, providing a broader understanding of electrical wiring colours in a global context.
International Wire and Cable Colours
Understanding different wiring colour standards is essential, especially for professionals working in international environments or with imported electrical equipment. Here’s a look at how wiring colours vary in some key regions:
Wiring Colours for the U.S.: The United States follows a different standard, with black for live wires, white for neutral, and green or bare copper for earth wires.
Wiring Colours for Canada: Canadian wiring colours are similar to the U.S., maintaining the same colour scheme for live, neutral, and earth wires.
Wiring Colours for Australia: Australian wiring standards also differ, with active (live) wires in brown or red, neutral wires in blue or black, and earth wires in green or green and yellow.
These differences highlight the importance of understanding and adhering to local wiring standards to ensure safety and compliance in electrical installations.
Recent Changes and Future Trends in Wiring Colours
In the UK, the most significant recent change in wiring colours occurred in 2004, aligning the UK with European standards. This transition to new UK wiring colours represents a commitment to safety and international harmonisation. Looking ahead, future trends in wiring standards may continue to evolve, influenced by technological advancements, safety research, and international collaboration. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for anyone involved in electrical work.
The global perspective on wiring colours underscores the diversity of electrical standards worldwide. Recognising these differences is key for professionals working in an increasingly interconnected world and for anyone dealing with international electrical systems.
Summarising Key Insights on UK Wiring Colours and Electrical Safety
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on UK old wiring colours, it’s important to reflect on the key insights and takeaways. This journey through the evolution of wiring standards, practical handling tips, and international comparisons underscores the critical role of wiring colours in electrical safety and compliance.
The Importance of Staying Informed
Staying informed about wiring colours and electrical standards is not just a technical necessity; it’s a safety imperative. As technology evolves and standards are updated, continuous learning and adaptation are key. Whether you’re a homeowner, a DIY enthusiast, or a professional electrician, being knowledgeable about wiring colours and their significance is integral to ensuring electrical safety.
Emphasising Safety and Professional Guidance
Finally, while this guide provides comprehensive information, it’s always recommended to seek professional advice for electrical installations and maintenance. Professional electricians are equipped with the expertise and understanding of the latest regulations to ensure safe and compliant electrical work.
In summary, understanding old and new wiring colours in the UK is more than just knowing a set of colour codes; it’s about ensuring the safety, functionality, and compliance of electrical systems in our homes and workplaces. By embracing these standards and staying informed, we contribute to a safer and more efficient electrical future.
Additional Resources for Further Reading
British Standards Institute (BSI): For the latest information on BS 7671 and other electrical standards.
Health and Safety Executive (HSE): Provides guidelines on electrical safety at home and in the workplace.
Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET): Offers detailed publications and resources on wiring regulations and electrical installation best practices.